HAVE TO FOR OBLIGATION
HAVE TO FOR OBLIGATION
¿Cuál es la
diferencia entre MUST y HAVE TO en inglés?
Una pregunta importante sobre la
gramática: ¿Cuál es la diferencia entre must y have to en inglés?
Mucha gente piensa que es sobre una obligación más fuerte y otra que es
más bien una sugerencia. Pero no es exactamente así.
Para hacer una sugerencia,
usamos should.
Unos ejemplos antes de seguir…
Usos de SHOULD para sugerencias
If you feel sick, you should go to the doctor.
If you really want to learn vocabulary, you should read more.
You should ask Tom. I’m sure he knows the answer.
Q: Do you think I should ask for a raise?
A: No, I think you should quit. You’ll find a better job.
Tengo más sobre should en mi otra página, en el curso gratuito de
inglés básico. Aquí lo tienes: Inglés Básico 21 – el verbo modal
should.
Aquí tienes el video donde puedes escuchar algunos de los siguientes
ejemplos:
La diferencia entre MUST y HAVE TO en inglés
Entonces, ¿cuál es la diferencia
entre must y have to?
Must se refiere a una obligación
entre dos personas, o una obligación que sientes.
Y have to se refiere
a una obligación externa… las reglas, la ley, algo que tienes que hacer y
punto. Normalmente en mis clases explico que have to es algo
que si no lo haces, hay consecuencias.
I have to get up early tomorrow. I have a meeting at 9 AM.
You have to get a visa if you want to work in Australia.
I have to pay my taxes this month.
They have to stay at work until they finish the project.
We have to leave now. If we don’t, we’ll miss our flight.
Todas estas frases son cosas que tienes que hacer. Si no, te pasará
algo. Si no consigues el visado, incumples la ley. Si no llegas a tiempo,
pierdes el vuelo. Si no vas a la reunión, tu jefe se enfada.
Cómo usar el auxiliar modal MUST en inglés
En cambio, must es una obligación
personal, una obligación impuesta por el hablante. Si digo I must es algo que siento, no algo que tengo que
hacer.
Y si digo you must no es una regla o la ley, sino algo que
quiero (fuertemente) que tu hagas. Una
obligación personal, no institucional.
You must come visit me when you’re in town.
I must go to bed. I’m exhausted.
When you go to Barcelona, you must visit the cathedral. It’s beautiful!
You must try that new Italian restaurant. The food is great!
I have a toothache. I must call the dentist to make an
appointment.
En todo caso, en el inglés escrito y
formal, se usa must también para obligaciones
externas que vienen de reglas, la ley, etc.
Por ejemplo, en un restaurante tipo fast food se podría ver un aviso así
en el baño:
Aquí tienes unos ejemplos del uso de must para obligaciones formales e
impersonales…
Ejemplos de MUST en inglés formal
Guests at the hotel must check out before 12 PM.
Employees must wash hands before returning to work.
Students must pass their exams in order to continue to the next grade.
All managers must present next year’s budgets before the end of the
month.
Citizens must present a valid photo ID in order to vote in the election.
Fíjate que ninguna de estas frases es
personal, de tú a tú. Son reglas, lo que tienen que hacer todos los estudiantes,
todos los empleados de una empresa, etc.
El otro uso de MUST para posibilidad
Los verbos modales en inglés normalmente hablan de posibilidad también,
y must habla de algo que supones que es muy probable – casi seguro.
Aquí tienes
unos ejemplos:
If he’s not at work, he must be on vacation.
I can’t find my keys. I must have lost them.
You lost your job? Oh no! You must be sad…
The bus must have left already. There’s nobody waiting.
I feel terrible. I must be getting sick.
Más sobre MUST y HAVE TO en inglés
Dicho todo eso, en inglés americano usamos have to mucho más que must.
Incluso para obligaciones personales, nos basta con have to.
Así que es otra cosa que voy a
decir no te preocupes. Hay matices, pero te puedes
comunicar sin obsesionarte con la diferencia entre obligación interna y
externa.
Hay mucho más que decir sobre los
verbos modales, y afortunadamente van a ser el tema del próximo mes en mis
lecciones premium Pasaporte al Inglés.
Vamos a ver, por ejemplo, la
diferencia entre las negaciones mustn’t y don’t have to, cómo formar pasados, cómo usar can, could, will, would, should, ought to y
mucho más.
Buen aprendizaje,
Los verbos modales son
ciertos verbos que son invariables, es decir, que se forman igual con
todas los pronombres personales. Sin embargo, el verbo 'have to' por sus
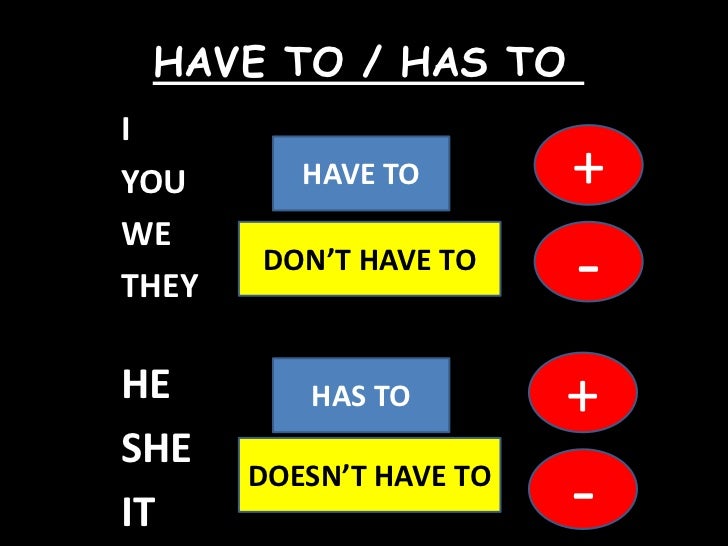
peculiaridades suele considerarse un semi-modal.
Tengo que estudiar
para el examen.
¿PARA QUÉ SIRVE?
Utilizamos el verbo ‘have to’ para expresar necesidad u
obligación externa, es decir, obligaciones impuestas por otros.
Tengo que estudiar
para el examen.
I have to study for
the exam.
¿CÓMO SE FORMA?
El verbo 'have
to' sigue las reglas propias
del Presente Simple, por lo que debemos tener en cuenta la tercera
persona del singular. Además, necesitamos los auxiliares para
formar la negativa y la interrogativa.
Tengo que estudiar
para el examen.
I have to study for
the exam.
Ella no tiene
que estudiar para el examen.
She doesn't have to study for the exam.
¿Tiene ella que abrir
la ventana?
Does she have to open the window?
¿QUÉ DEBO RECORDAR?
Los aspectos importantes que debemos tener en cuenta
son los siguientes:
- Recuerda que ‘have to’ suele compararse con
‘must’ y ambos pueden traducirse por ‘tener que’ o ‘deber’.
- Utilizamos
el verbo ‘have to’ como cualquier verbo, por lo que necesitamos
recordar las formas del Presente Simple.
- También
puede encontrarse como ‘have got to’, y en ese caso seguiremos las reglas
del ‘have got’
Ejemplos:
1. She has to take the children with her to Houston. (Ella tiene
que llevar a los niños con ella a Houston)
2. He has to lend us the money which we need. (Él tiene que
prestarnos el dinero que necesitamos)
3. She has to be back by noon. (Ella tiene que regresar para
mediodía)
4. She has to return later. (Ella tiene que regresar más tarde)
5. You have to learn at least five new words every day. (Tú tienes que
aprender al menos cinco palabras cada día)
6. You have to call her tomorrow. (Tú la tienes que llamar mañana)
7. You have to see her tomorrow. (Tú tienes que verla mañana)
8. They have to help you with your work. (Ellos tienen que
ayudarte con tu trabajo)
9. You have to go by plane. (Tú tienes que ir en avión)
10. It has to rain this evening. (Tiene que llover esta tarde)
11. He has to spend more time on his homework. (Él tiene
que invertir más tiempo en su tarea)
EJERCICIOS
MUST
VS. HAVE TO
Completa las frases con must, mustn't,
have to, don't / doesn't have to.
El verbo "have" es un verbo muy importante y si quieres aprender a manejarlo te invitamos a leer sobre Verbo have en pasado simple, pero en el contexto: Es usual que uno de los principales verbos que estudiemos en el inglés sea el verbo “have”; este refiere directamente a la acción de tener algo y expresa, a través de una oración bien estructurada, aquello que el sujeto de nuestra oración se encuentra ejecutando de manera directa.
ResponderBorrarEl pasado simple, busca expresar a través de su estructura una acción que ya no está siendo realizada en el presente, cuyo tiempo ya pasó; sin embargo, no existe un tiempo límite para hacer uso del pasado simple del verbo have en una oración. La acción puede haber sido, hace 5 minutos o 5 años, la estructura seguirá siendo igual.